ASP.NET includes a control named FileUpload that allows website users to upload files to the web server. The FileUpload control manages the posted file data, by examining it, disregarding it, or saving it to a back-end database or a file on the web server. The FileUpload control represents the <input type = “file”> HTML tag and you can use it through the control tag:
<asp:FileUpload ID=”Uploader” runat=”server” />
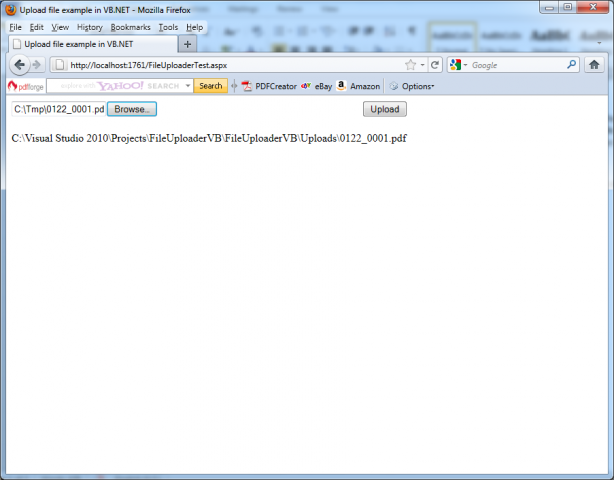
The next picture shows a complete web page that demonstrates how to upload a user-specified file. This example allows the upload of only those files with the extensions .pdf, .doc,.xls and .ppt.
Here’s the markup for the upload page:
<%@ Page Language=”vb” AutoEventWireup=”false” CodeBehind=”FileUploaderTest.aspx.vb”
Inherits=”FileUploaderVB.FileUploaderTest” %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN” “https://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd”>
<html xmlns=”https://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml”>
<head runat=”server”>
<title>Upload file example in VB.NET</title>
</head>
<body>
<form id=”form1″ runat=”server”>
<div>
<asp:FileUpload ID=”Uploader” runat=”server” Width=”512px” />
<asp:Button ID=”btnUpload” runat=”server” Text=”Upload” OnClick=”btnUpload_Click” />
<br />
<br />
<asp:Label ID=”lblInfo” runat=”server”></asp:Label>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Here’s the VB.NET code for the upload page:
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Linq
Imports System.Web
Imports System.Web.UI
Imports System.Web.UI.WebControls
Imports System.IO
Public Class FileUploaderTest
Inherits System.Web.UI.Page
Private UploadDir As String
Protected Sub Page_Load(ByVal sender As Object, ByVal e As System.EventArgs) Handles Me.Load
‘ Place files in a website subfolder named Uploads.
UploadDir = Path.Combine(Request.PhysicalApplicationPath, “Uploads”)
End Sub
Protected Sub btnUpload_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnUpload.Click
‘Check that a file is actually being submitted.
If Uploader.PostedFile.FileName = “” Then
lblInfo.Text = “You do not specify a file.”
Else
‘ Check the extension.
Dim Ext As String = Path.GetExtension(Uploader.PostedFile.FileName)
Dim SrvFName As String = “”
Dim FullUpldPath As String = “”
Select Case Ext.ToLower()
Case “.pdf”, “.doc”, “.xls”, “.ppt”
‘ Using this code, the saved file will retain its original
‘ file name when it’s placed on the server.
SrvFName = Path.GetFileName(Uploader.PostedFile.FileName)
FullUpldPath = Path.Combine(UploadDir, SrvFName)
Case Else
lblInfo.Text = “This file type is not allowed.”
Return
End Select
Try
Uploader.PostedFile.SaveAs(FullUpldPath)
lblInfo.Text = “File ” + SrvFName
lblInfo.Text += ” uploaded successfully to” + FullUpldPath
Catch ex As Exception
lblInfo.Text = ex.Message
End Try
End If
End Sub
End Class
Notes:
– The saved file keeps its original (client-side) name. The code uses the Path.GetFileName() static method to transform the fully qualified name provided by FileUpload.PostedFile.FileName and retrieve just the file, without the path.
– The FileUpload.PostedFile object contains only a few properties. One interesting property is ContentLength, which returns the size of the file in bytes. You could examine this setting and use it to prevent a user from uploading excessively large files.