You can use WindowsPrincipal class to access WindowsIdentity object through the Identity property. You need this when your project is based on Windows authentication and you use in your code User property which returns an IPrincipal object as instance of the WindowsPrincipal class. The class implements four overloads of IsInRole() that all check whether the user is in a specified Windows user group:
– IsInRole(string) is used to accept the name of the checked Windows user group.
– IsInRole(int) expects an integer Role Identified (RID) that refers to a user group.
– IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole) expects a member of the WindowsBuiltInRole enumeration ( see the table bellow )
– IsInRole(SecurityIdentifier) expects the specified security identifier (SID) which belongs to the Windows user group.
You can use the next code lines to test if the user is in a predefined Windows role:
Imports System.Security.Principal
‘ … other code is omitted
If (Request.IsAuthenticated) Then
lblInfoText.Text = “<b>Name: </b>” + User.Identity.Name
If TypeOf (User) Is WindowsPrincipal Then
‘ You must cast the User object to a WindowsPrincipal to access this Windows-specific functionality.
‘This cast will not work with forms authentication enabled and with the roles API enabled
Dim Principal As WindowsPrincipal = DirectCast(User, WindowsPrincipal)
lblInfoText.Text += “<br><b>SystemOperator? </b>”
lblInfoText.Text += Principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.SystemOperator).ToString()
End If
End If
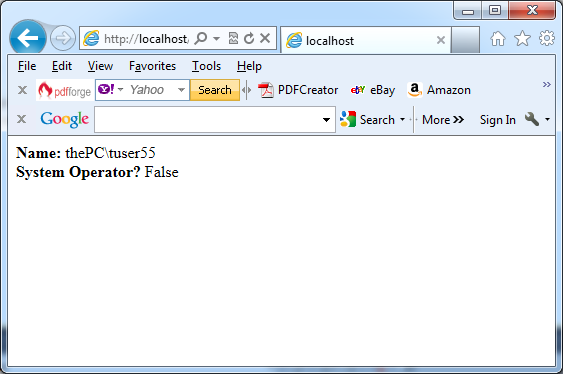
The next picture shows the result:
The next table lists possible values for the WindowsBuiltInRole enumeration:
| Role |
Description |
| AccountOperator | Users with the special responsibility of managing the user accounts on a computer or domain. |
| Administrator | Users with complete and unrestricted access to the computer or domain. |
| BackupOperator | Users who can override certain security restrictions only as part of backing up or restoring operations. |
| Guest | Like the User role but even more restrictive. |
| PowerUser | Similar to Administrator but with some restrictions. |
| PrintOperator | Like a User but with additional privileges for taking control of a printer. |
| Replicator | Like a User but with additional privileges to support file replication in a domain. |
| SystemOperator | Similar to Administrator but with some restrictions. Generally, system operators manage a particular computer. |
| User | Users are restricted accounts that are prevented from making system-wide changes. |